
Bariatric Chair: A Practical Guide for Healthcare, Offices, and Senior Living
Key Takeaways
-
A bariatric chair is specialized seating engineered to support individuals with higher body weights, typically rated from 500 lbs up to 1000 lbs of evenly distributed weight.
-
These chairs feature reinforced steel frames, wider seats (often 24”–30” or more), and antimicrobial vinyl upholstery for easy cleaning and infection control in medical environments.
-
Common applications include waiting rooms, patient rooms, resident lounges, rehabilitation areas, and office workstations where safe sit-to-stand transfers are essential.
-
Staff and caregiver benefits include reduced injury risk during patient handling, improved ergonomics, and enhanced dignity and comfort for larger users.
-
Bariatric seating is part of a broader furniture program that can include coordinated sofas, recliners, dining chairs, and lounge seating designed to meet the needs of diverse populations.
What Is a Bariatric Chair?
A bariatric chair is a high-capacity seating solution specifically engineered for people who exceed standard weight ranges. These chairs typically support at least 500 lbs, with advanced models rated up to 1000 lbs of evenly distributed weight. The term “bariatric” originates from medical terminology related to the treatment of obesity and has become widely used across hospitals, clinics, and senior living communities.
It’s important to understand that bariatric chairs are not simply oversized versions of standard furniture. They are designed with reinforced structures, wider seats, and stability features that safely accommodate larger body sizes. The engineering behind these chairs accounts for factors like frame durability, seat geometry, and weight distribution that standard seating cannot address.
Examples of bariatric seating include:
-
Bariatric guest chairs for waiting rooms and reception areas
-
Heavy duty office chairs for workstations and administrative spaces
-
Bariatric lounge chairs for resident common areas in senior living
-
Bariatric hip chairs for post-surgical recovery and rehabilitation
In healthcare and senior living settings, bariatric chairs are often specified alongside bariatric beds, commodes, and wheelchairs as part of a comprehensive care plan. This integrated approach ensures that larger users have appropriate support at every touchpoint throughout their day.

Key Design Features of Bariatric Chairs
Understanding the structural and ergonomic elements that distinguish bariatric chairs from standard seating helps facility managers and designers make informed purchasing decisions. These features directly impact safety, comfort, and durability across healthcare and senior living environments.
Weight Capacity Ratings
Typical weight ratings for bariatric models include 500 lbs, 750 lbs, 800 lbs, and 1000 lbs. Many manufacturers align their testing with ANSI/BIFMA or equivalent safety and durability standards. When reviewing product details, always verify the rated capacity is based on evenly distributed weight rather than peak load testing.
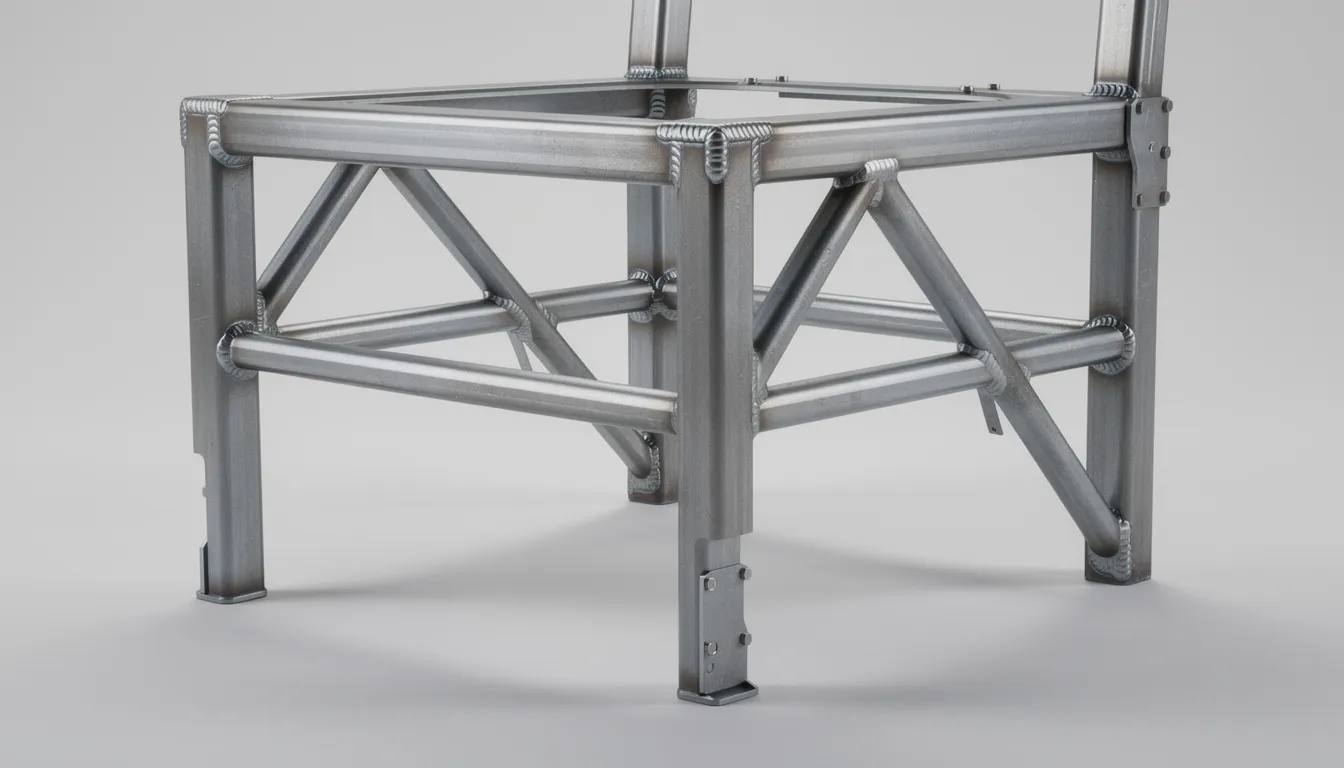
Frame Construction
The frame is the foundation of any bariatric chair. Key construction elements include:
-
Heavy-duty tubular or solid steel frames
-
Reinforced welded joints and gusset plates
-
Seven-leg bases on task chairs for superior stability compared to standard five-leg designs
-
Anti-tip bars and wide stance configurations
-
Optional hardwood components for residential aesthetics in senior living lounges
Seat Dimensions
Bariatric chairs feature seat specifications designed to accommodate larger body types:
|
Feature |
Standard Chair |
Bariatric Chair |
|---|---|---|
|
Seat Width |
18”–20” |
24”–30”+ |
|
Seat Depth |
16”–18” |
18”–22” |
|
Weight Capacity |
250–300 lbs |
500–1000 lbs |
|
Seat Height Range |
16”–20” |
17”–24” |
Front edge shaping reduces pressure on thighs and improves circulation during extended sitting periods. Tuned seat depth minimizes sliding between cushions and legs, which is particularly important for users with limited mobility.
Upholstery and Infection Control
Material selection is critical in medical offices and senior living facilities:
-
Antimicrobial vinyl upholstery resists bacteria, mold, and mildew
-
Medical-grade polyurethane withstands repeated cleaning with hospital disinfectants
-
High-performance fabrics resist stains and bodily fluids
-
Minimal seam design reduces areas where contaminants can collect
Comfort Features
Despite their heavy duty construction, bariatric chairs prioritize user comfort:
-
Thick, high-density foam cushions that maintain shape over time
-
Contoured backrests with integrated lumbar support
-
Padded arms that provide leverage for sit-to-stand transfers
-
Adjustable tilt, height, and tension controls on task models
Stability and Floor Protection
Features that protect both users and flooring include non-skid glides, wide stance legs or sled bases to prevent tipping, and adjustable leveling glides for uneven floors. These elements ensure the chair remains stable during transfers and daily use.
Bariatric Chairs in Healthcare Settings
Hospitals, clinics, and medical offices increasingly specify bariatric chairs as part of inclusive patient and visitor seating programs. With approximately 13% of the global adult population classified as obese, the demand for appropriate seating has become a standard consideration rather than a special accommodation.
Waiting Rooms and Reception Areas
Heavy-duty guest chair options in lobbies ensure every patient can sit safely and discreetly. Many facilities arrange rows of standard seating with clearly designated bariatric options rated at 750–1000 lbs strategically placed throughout the room. This approach allows larger users to choose appropriate seating without drawing unwanted attention.
Exam and Treatment Room Seating
Sturdy side chairs with supportive arms serve multiple purposes:
-
Support patient transfers to and from exam tables
-
Allow clinicians to work at appropriate heights
-
Tolerate frequent cleaning with hospital-grade disinfectants
-
Provide comfortable seating during consultations
Treatment chairs designed for patients with BMI over 30 often include features like manual or electric recline, stand-assist mechanisms, and adjustable positioning to reduce pressure sores and improve caregiver ergonomics.
Infection Control Considerations
Easy cleaning is essential in healthcare environments. Antimicrobial vinyl surfaces, smooth construction with minimal crevices, and compatibility with standard disinfectants allow rapid wipe-down between patients. Many facilities stock chairs with clean-out gaps between seat and back to simplify maintenance.
Staff and Caregiver Safety
Bariatric hip-style chairs with sturdy arms and higher seat heights assist with sit-to-stand transitions, reducing strain on nurses, physiotherapists, and aides. Motorized adjustment features in some models limit manual handling and reduce injury risks for both patients and staff.
Emergency Departments and Imaging Suites
These high-acuity areas with longer waiting times require durable seating that can accommodate diverse patient populations. Bariatric options in X-ray, CT, and MRI waiting areas ensure all patients receive appropriate support regardless of body size.
Many healthcare systems standardize bariatric furniture specifications across facilities, same frame style in 500, 750, and 1000 lb ratings for a consistent look and simplified purchasing.
Bariatric Seating in Senior Living and Long-Term Care
Senior living communities and long-term care homes use bariatric chairs to support residents with limited mobility, chronic conditions, and higher body weights. The goal is creating an environment where all residents can participate fully in daily activities with dignity.
Resident Room Applications
Bariatric armchairs in private rooms feature:
-
Supportive arms that provide leverage for independent transfers
-
Wider seats that accommodate larger body sizes comfortably
-
Higher seat heights (often 20”–24”) that facilitate transfers from bed to chair
-
Durable construction that withstands daily use
Common Area Uses
Bariatric lounge seating, dining chairs, and activity-room chairs are designed to visually match standard furniture while quietly offering higher weight ratings and wider dimensions. This coordinated style approach ensures residents can use any space in the facility without feeling singled out.
Dignity and Social Inclusion
When residents can sit in dining rooms, lounges, and outdoor spaces alongside peers without needing visibly “special” institutional furniture, their sense of belonging and self-worth improves. This perfect integration supports mental health and encourages participation in community activities.
Orthopedic and Rehabilitation Benefits
Bariatric hip chairs and sit-to-stand friendly designs protect post-surgical joints, particularly after hip and knee replacements. These chairs support physiotherapy programs by providing stable, comfortable seating that encourages proper posture and safe transfers.
Durability for 24/7 Operations
Senior living operators need furniture constructed for continuous use:
-
Frames designed for repeated transfers throughout the day
-
Reinforced joints that withstand years of heavy use
-
Replacement cushion options to extend product lifecycle
-
Easy maintenance that doesn’t disrupt resident schedules

Types of Bariatric Chairs and Seating Solutions
Bariatric seating is available in several categories to address different functions across healthcare, office, and senior living environments. Understanding these options helps facility planners create comprehensive seating programs.
Bariatric Guest and Waiting Room Chairs
These chairs serve lobbies, clinics, and diagnostic centers with:
-
Armless and armed options for flexibility
-
Wide seats that accommodate diverse body types
-
Fixed height for simplicity and durability
-
Simple, durable construction that requires minimal maintenance
-
Options for assembly required or ready-to-use delivery
Bariatric Office and Task Chairs
For workers who spend extended periods at desks, adjustable gas lift models support 350–500+ lbs with:
-
Reinforced bases and heavy-duty cylinders
-
Tilt and tension controls for personalized positioning
-
Larger seat and back proportions for all-day comfort
-
Lumbar support and ergonomic adjustments
-
Good mobility for navigating office space
Bariatric Hip Chairs
Designed for orthopedic and post-surgical patients, these chairs feature:
-
Elevated seat height for easier sit-to-stand transitions
-
Shallow seat depth that keeps feet flat on the floor
-
Supportive arms that provide leverage without strain
-
Configurations that meet rehabilitation protocol requirements
Bariatric Recliners and Lounge Chairs
Used in infusion clinics, patient rooms, and senior living lounges, these models offer:
-
Extended footrests for circulation and comfort
-
Easy lever operation for users and caregivers
-
Locking mechanisms for safe transfers
-
Options for power positioning in advanced variants
Bariatric Dining and Side Chairs
Upright posture chairs with sturdy frames provide:
-
Clearance to fit under standard-height tables
-
Broader seat width without excessive overall dimensions
-
Construction that supports daily use in high-traffic dining environments
Many projects specify a mix of these types so larger users have appropriate seating at every touchpoint from admission desks and family lounges to therapy gyms and cafeterias.
Outfitting a clinic, senior living community, or office? The fastest way to improve comfort, safety, and inclusivity is to make sure high-capacity seating is always available in waiting rooms, resident lounges, and anywhere sit-to-stand transfers happen.
Explore our Bariatric Chair selection to find options with:
- 500–1000 lb weight ratings (evenly distributed)
- Wider seats and reinforced frames for stability and durability
- Supportive arms for safer transfers
- Healthcare-ready upholstery designed for easy cleaning
How to Choose the Right Bariatric Chair
Selecting appropriate bariatric seating requires a systematic approach that accounts for user needs, space constraints, and operational requirements. This step-by-step guide helps facility managers, designers, and clinicians make informed decisions.
Step 1: Define Weight and Size Requirements
-
Review population data and clinical records to understand current needs
-
Gather staff input on patients or residents who require enhanced support
-
Decide whether 500, 750, or 1000 lb chairs are needed
-
Determine quantities for each weight range across facility areas
Step 2: Measure Your Space
Before you purchase, consider:
-
Door widths and corridor dimensions
-
Room layouts and circulation paths
-
Table clearances and furniture arrangements
-
Exit routes and emergency egress requirements
Chair width and depth must allow safe movement without obstructing traffic flow.
Step 3: Evaluate Comfort and Ergonomics
-
Seat height relative to user population (older adults often need slightly higher seats)
-
Armrest shape and strength for push-off during transfers
-
Back support features for users who sit for extended periods
-
Range of adjustability on task and office models
Step 4: Prioritize Material and Infection Control
Select upholstery that meets your environment requirements:
-
Antimicrobial vinyl compatible with approved disinfectants
-
Fluid-resistant surfaces that support clean protocols
-
Materials tested for durability under repeated cleaning
-
Manufacturer verification of cleaner compatibility
Step 5: Consider Aesthetics
-
Choose finishes and silhouettes that coordinate with existing furniture
-
Select styles that integrate into the environment rather than standing out
-
Match frame colors and upholstery to room décor where possible
Step 6: Involve End Users
-
Gather feedback from nursing staff and occupational therapists
-
Include resident or family councils in evaluation processes
-
Conduct trials with sample chairs before large-scale purchase
-
Add items to cart for approval once feedback is collected
Step 7: Review Purchasing and Lifecycle Factors
|
Factor |
Questions to Ask |
|---|---|
|
Warranty |
What’s covered? For how long? |
|
Parts Availability |
Can cushions and components be replaced? |
|
Lead Times |
Is the product in stock or made to order? |
|
Standardization |
Can supplier provide matching standard and bariatric models? |
Bariatric Furniture Beyond Chairs
Bariatric chairs are often part of a larger furniture strategy in healthcare and senior living facilities. A comprehensive approach ensures consistent support throughout the environment.
Complementary Furniture Types
-
Bariatric sofas and loveseats for family lounges and visitor areas
-
High-capacity recliners for patient rooms and overnight stays
-
Bariatric sleeper chairs for family members staying with patients
-
Sturdy bench seating in corridors and transition spaces
Dining and Cafeteria Furniture
Reinforced tables designed to work with bariatric chairs safely support heavier loads while maintaining adequate knee and leg clearance. These tables feature durable bases and surfaces that tolerate daily use in high-traffic dining environments.
Integration with Mobility Equipment
Modern bariatric seating is designed to work alongside:
-
Ceiling lifts and floor lifts
-
Transfer devices and sling systems
-
Wheelchairs and transport chairs
-
Physical therapy equipment
This integration improves workflow efficiency and reduces injury risk for caregivers.
Planning Benefits
Standardizing bariatric seating and furniture across a campus or network offers several advantages:
-
Easier movement of items between rooms and facilities
-
Guaranteed bariatric options in every public area
-
Simplified maintenance and replacement processes
-
Consistent aesthetics throughout the environment
Inspired designers and facility planners should consider bariatric furniture early in renovation or new build projects rather than treating it as an afterthought. This sustainable approach reduces long-term costs and ensures comprehensive accessibility from day one.
FAQ
What weight capacity should I look for in a bariatric chair?
Many facilities start with 500 lb rated chairs for general use, while emergency departments, surgical units, and bariatric programs often add 750–1000 lb models based on their patient population. It’s generally safer to choose a slightly higher capacity than current average needs to account for future demographic changes and reduce replacement frequency. Always verify manufacturer specifications and ensure the rated capacity applies to evenly distributed weight.
How is a bariatric chair different from a standard “big and tall” chair?
Big and tall office chairs focus mainly on comfort for individual users in typical workplace settings, while bariatric chairs are engineered specifically for healthcare and senior living with reinforced frames, infection control upholstery, and compliance with medical or commercial standards. Bariatric models typically offer higher weight ratings, wider seats, and features that support assisted transfers and frequent cleaning with hospital-grade disinfectants.
Can bariatric chairs be used by smaller or average-size users?
Most bariatric chairs are safe for users of all sizes, but the seat width and height may feel oversized for some people, particularly in task or desk seating. Many facilities address this by mixing standard and bariatric chairs in shared spaces, allowing everyone to choose the option that fits them best without drawing attention to any individual. This way creates an inclusive environment where comfortable seating is available for all.
How do I clean and disinfect bariatric chairs in medical environments?
Cleaning protocols should follow your facility’s infection control guidelines, typically involving approved hospital-grade disinfectants used according to manufacturer dwell times. Most healthcare-grade bariatric chairs use antimicrobial vinyl or similar surfaces specifically tested for resistance to common cleaners. Always verify compatibility between your cleaning products and the chair manufacturer’s instructions on the product page to protect the upholstery and maintain warranty coverage.
Are bariatric chairs more expensive, and are they worth the investment?
Bariatric chairs generally cost more than standard seating due to reinforced construction and medical-grade materials, but they deliver significant value through reduced liability, lower injury risk for staff during transfers, and improved comfort and dignity for larger users. Many organizations treat bariatric seating as essential infrastructure, budgeting for it in capital projects and viewing it as a long-term safety and inclusion investment that pays dividends in patient satisfaction and staff retention.
Contact Us
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
!









